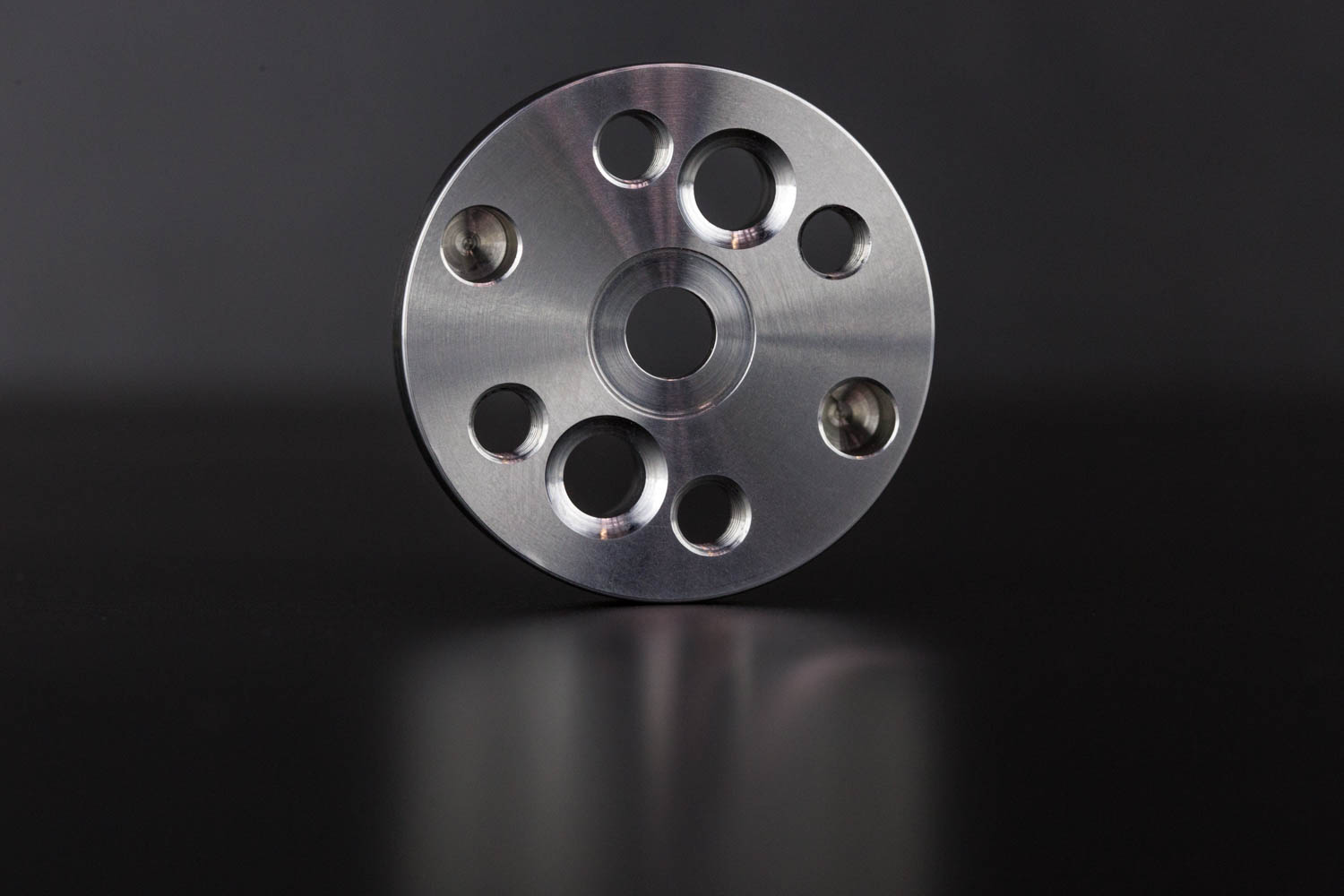
Mold making is the process used to duplicate three dimensional models or objects. A model is any object that has depth and an original model can be made from almost anything. If you were making your own object to mold you might use clay rock or plastic. Through the use of a mold making material a negative or a reverse of a model part is made the negative can then be used to cast a second part that is the same size and shape as the original part.

Injection moulding is a manufacturing process that allows for parts to be produced in large volumes. It works by injecting molten materials into a mould (or ‘mold’ in the United States). It is typically used as a mass production process to manufacture thousands of identical items. Injection moulding materials include metals glasses elastomers and confections although it is most commonly used with thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001
FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001
First of all we need to receive your 3D drawings (stp step igs iges format) and quote according to your needs such as quantity material surface finish etc.
Before the mold is assembled to the injection molding machine the drawing needs to be programmed so that we can clearly see the process of the material as it enters the mold for further adjustments and modifications.
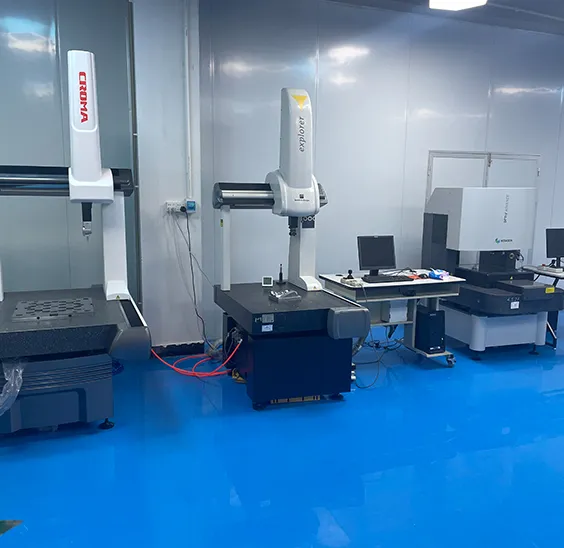
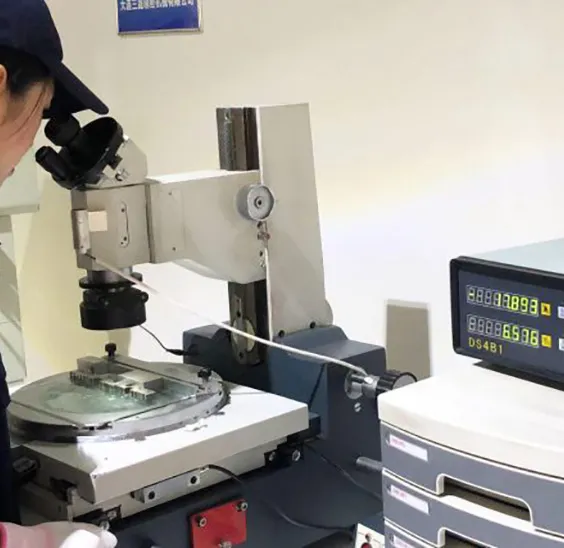
After the metal or plastic injection molding is determined it is put into production. After confirming the molding model with the customer the precision inspection and surface treatment are carried out.
After the mold is complete it is assembled into the injection molding machine. During the injection process we check that the machine is functioning properly (or not) make some necessary tool adjustments and generate a new sample.
After the samples are surface treated as specified by the customer they will be checked again for dimensions.
According to customer requirements choose the surface treatment method. At the same time quality inspection work is carried out.
The last step is to check whether the mold needs to be adjusted according to the analysis of the sample and whether the test sample meets the previous requirements.
After the samples have been tested to meet the preliminary requirements the samples can be packaged and shipped.
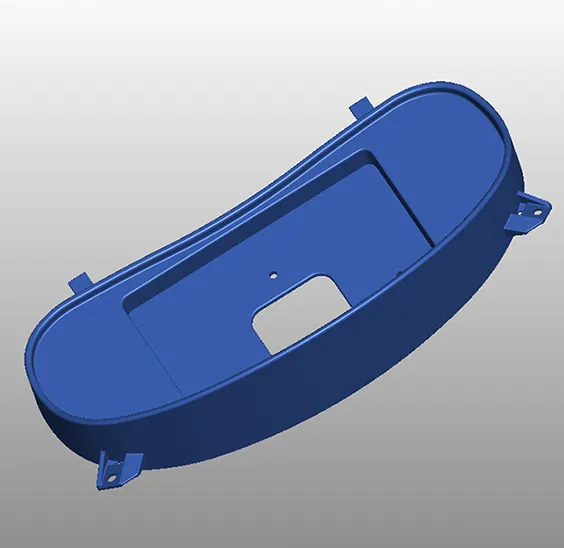
Injection molding is two large metal mold halves coming together a plastic or rubber material is injected into the cavity they form. Even though the plastic materials being injected are melted they aren’t really heated; the material is pressed into the injection ports (called gates) via a large auger screw. As the material is compressed it heats and begins to flow into the molds. Once it cools the two halves separate again and the part pops out. Repeat ten thousand times and you have a run of injection molded parts ready for use.
A wide variety of industries benefit from the highly versatile process of injection molding including: Medical & Pharmaceutical Eletronics Construction Food & Beverage Automotive Toys Agriculture Consumer Goods Sporting Goods
Injection molding is a fast cost effective and highly precise manufacturing process used for mass producing complex molded parts in a variety of materials including thermoplastics polymers aluminum and glass.
There are several types of injection molding processes including: Custom plastic injection molding Overmolding Insert molding Cube molding Die casting Gas-assisted injection molding Liquid silicone rubber injection molding metal injection molding Micro injection molding Reaction injection molding
How long an injection mold can last depends on several factors: mold material number of cycles operating conditions and time between production runs. The life expectancy of an injection mold can range from 1M+ cycles to less than 500 cycles based on the above criteria.
Although quite similar the difference between forming and molding comes down to their unique features and benefits depending on the application they are being used for. Injection molding is more suitable for large production runs of small intricate parts and involves injecting liquid polymers into a mold using extreme pressure and temperatures. Thermoforming also referred to as vacuum forming is more suitable for shorter production runs of large-scale designs and involves forming heated plastic sheets to a mold's surface.
ABS is a low-cost engineering plastic widely used for pre-injection molding prototypes.
Consult now
In high-stress or high-temperature applications PEEK is a great lightweight plastic substitute for most soft metals. Additionally PEEK is resistant to moisture wear and chemicals.
Consult now
Acrylic is a scratch-resistant plastic material often used for tanks panels and optical applications.
Consult now
Polypropylene (PP) resists most solvents and chemicals which makes it a wonderful material to manufacture laboratory equipment and containers for a variety of applications. PP also offers good fatigue strength.
Consult now
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a slippery plastic that is often machined into plugs and seals. It is also an excellent electrical insulator as well as being moisture and chemically-resistant.
Consult now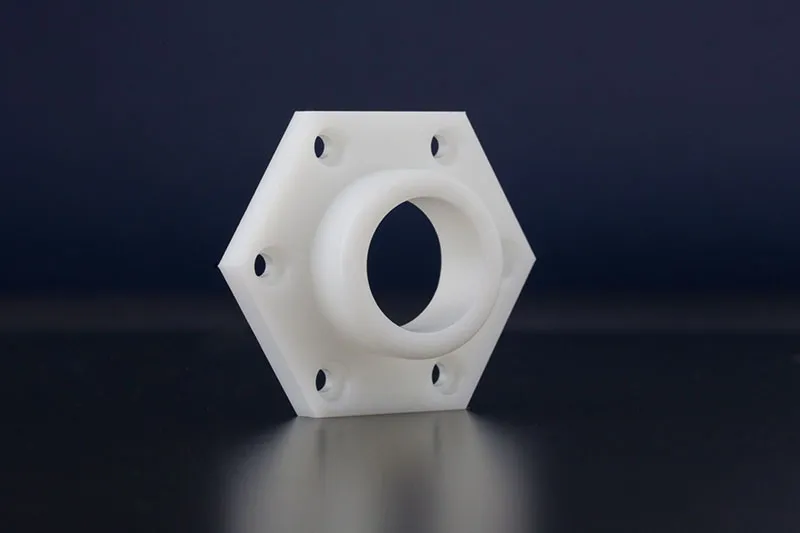
Delrin or acetal is a low-friction high-stiffness plastic material. With a relatively high toughness and minimal elongation Delrin boasts excellent dimensional accuracy.
Consult now
Nylon is a general purpose plastic material that resists both frictional and chemical wear. Two of the most notable use cases for Nylon are in medical devices and electronics insulation notably screws and spacers for panel mounted circuit boards.
Consult now
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance engineering plastic with excellent temperature resistance dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties.
Consult now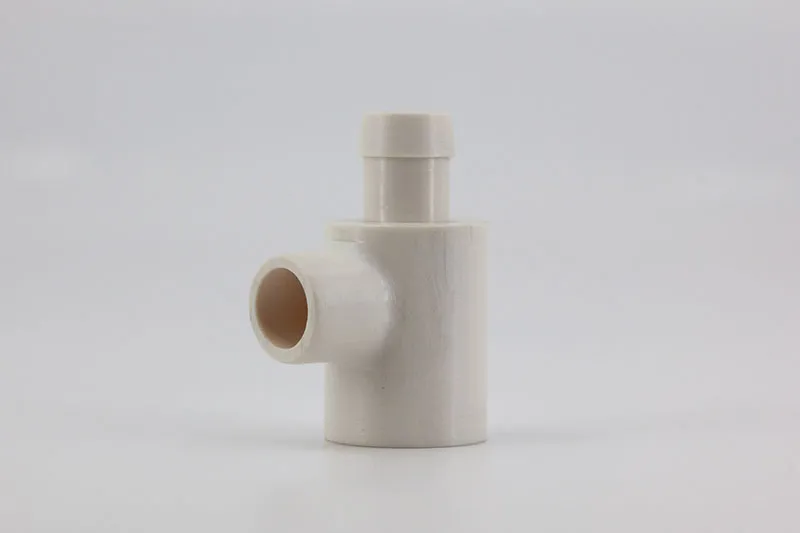
Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (or UHMW) is a hard plastic with a slippery surface which resists abrasion and wear. Additionally it offers high impact strength and is the optimal material for chute/hopper liners and machine guards.
Consult now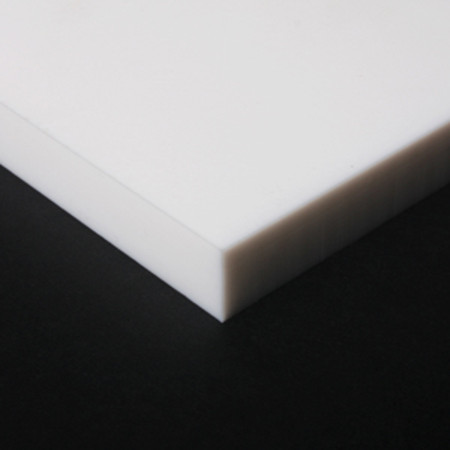
ULTEM 1000 is a translucent amber colored plastic with excellent durability strength stiffness and heat resistance. ULTEM 1000 may be selected over Nylon or Delrin because it has the highest dielectric properties. Common applications include industrial equipment medical devices and electronics.
Consult now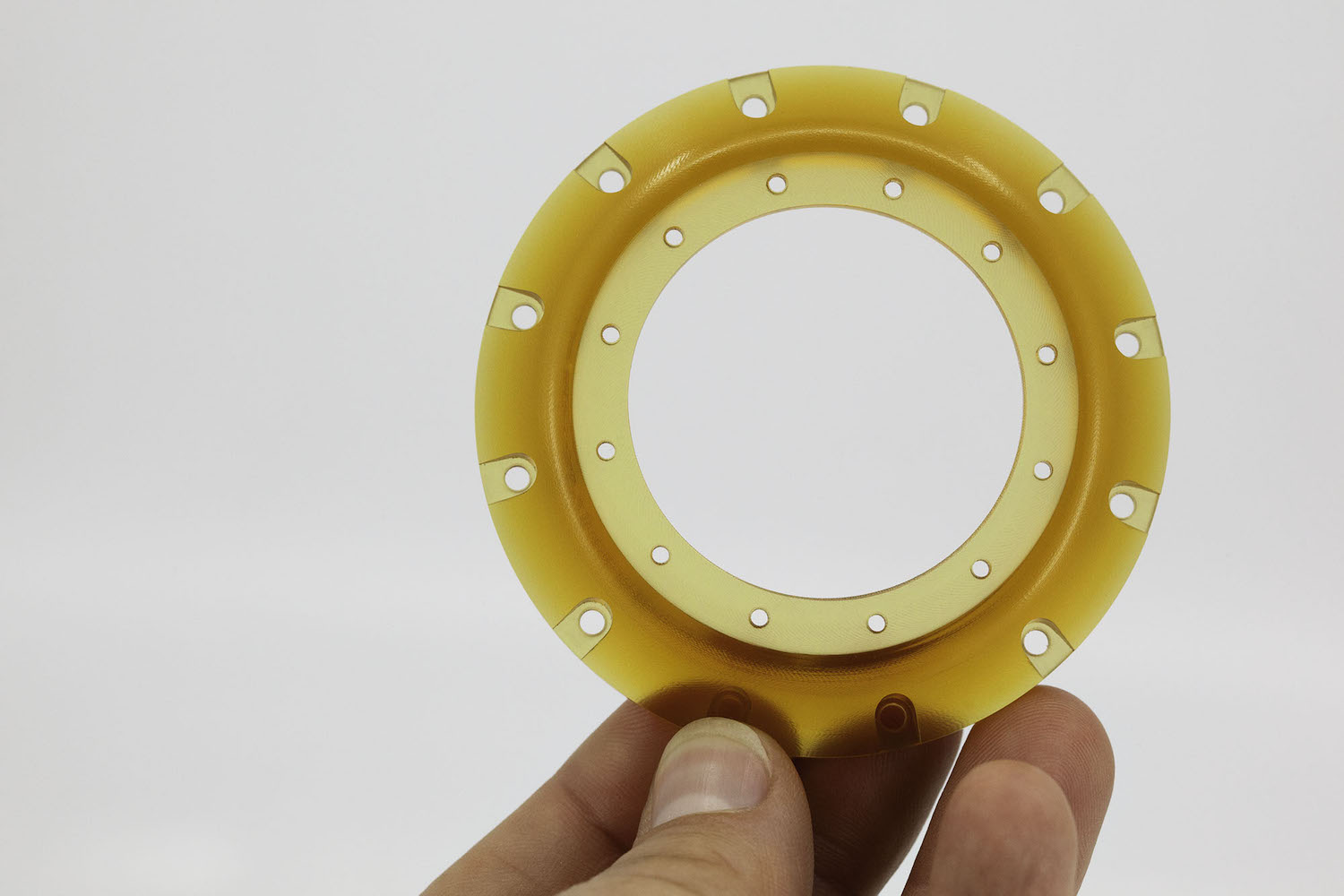
Garolite G-10 (also known as phenolic and epoxy-grade industrial laminate) is a composite material with a low coefficient of thermal expansion. It does not absorb water and is an excellent insulator making it useful for electronics applications.
Consult now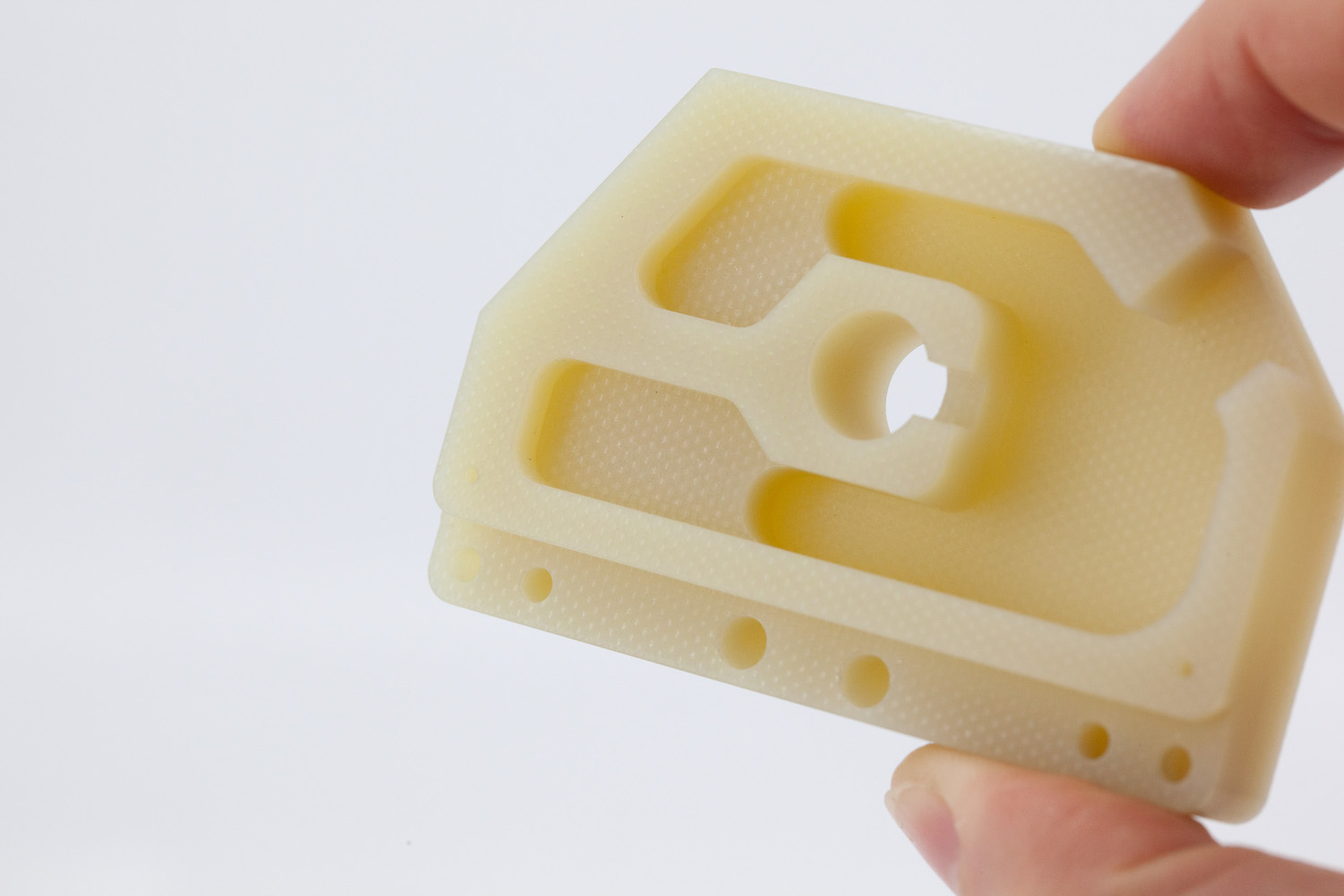
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used metals in the world because of its excellent strength-to-weight ratio low cost and recyclability.
Consult now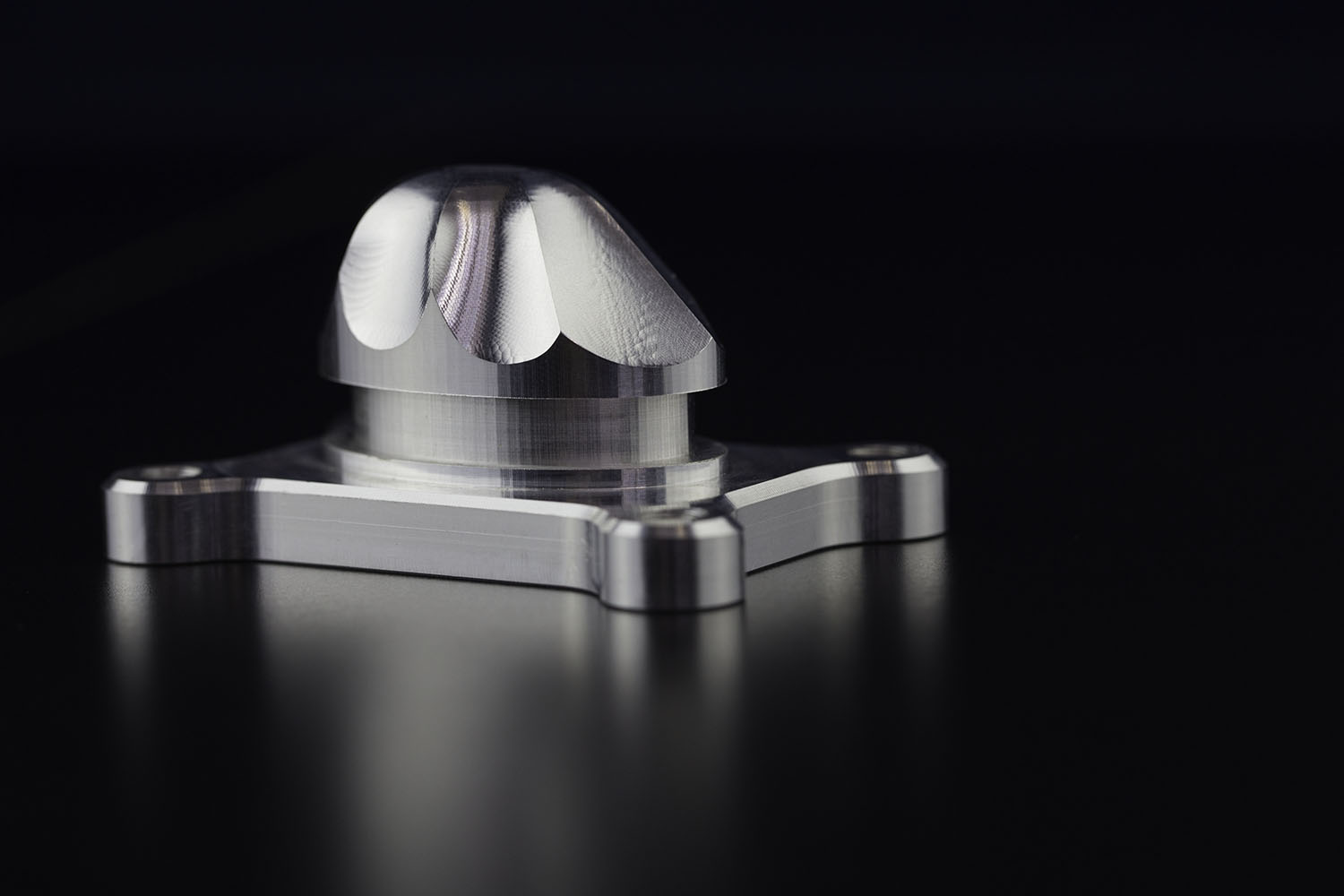
Zinc alloy has low melting point good fluidity easy fusion welding brazing and plastic processing corrosion resistance in the atmosphere blind material is easy to reuse and remelting suitable for die-casting instruments automobile parts casings etc.
Consult now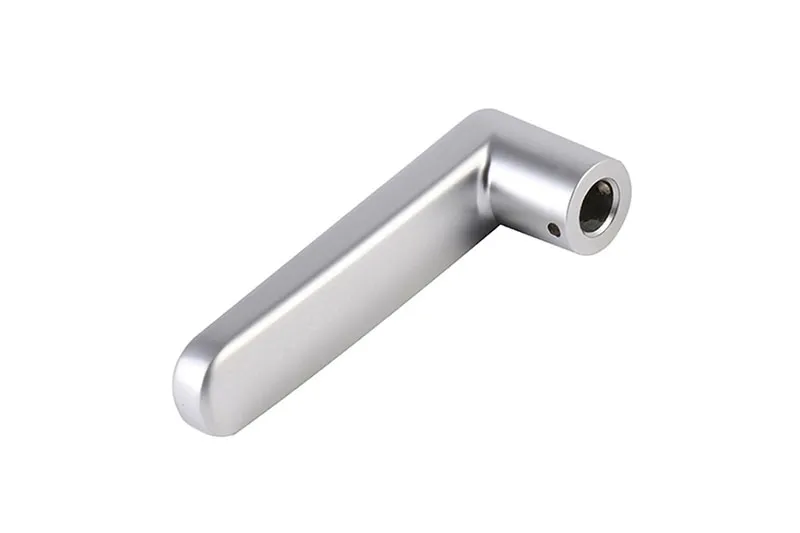
Cast iron is a dependable wear-resistant material that’s ideal for absorbing vibrations. Great for gears bases pulleys and bushings.
Consult now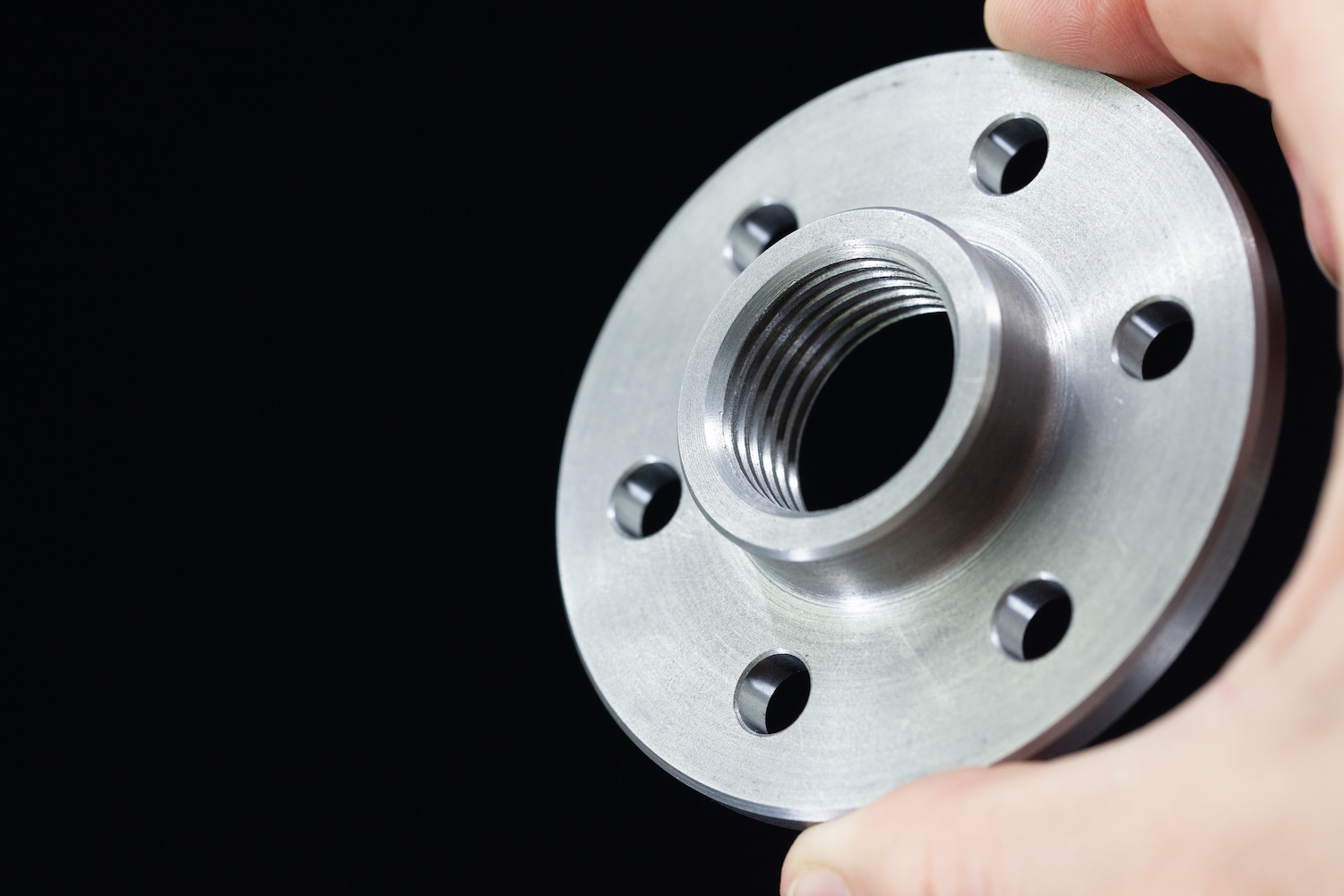
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and rust making it suitable for situations where a part may be exposed to the elements for long period of time. Stainless steel is also fairly malleable and ductile.
Consult now