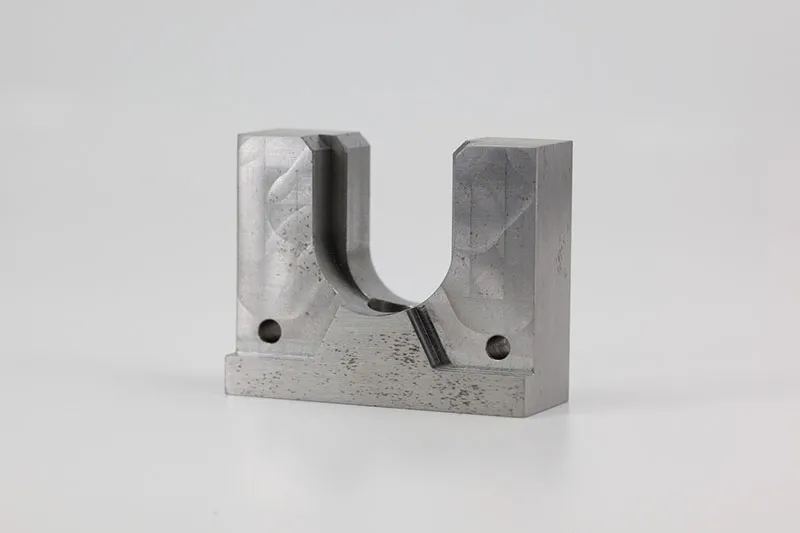
Vacuum casting is a casting process for elastomers using a vacuum to draw the liquid material into the mold. This process is used when air entrapment is a problem there are intricate details or undercuts or if the material is fiber or wire reinforced.

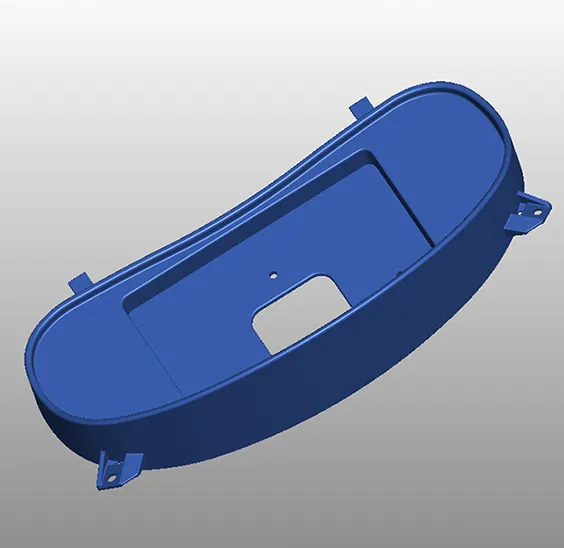
Rapid prototyping (RP) quickly creates a physical part directly from its CAD model data using various manufacturing techniques. Rapid prototyping can be used at any stage of the product development cycle for any components or sub-components.

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001
FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001

FDIS09001-2015A
IATF-16949
ISO-27001
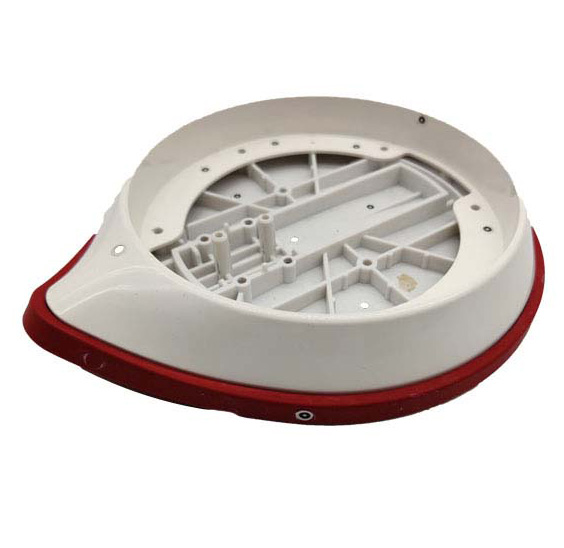
First of all we need to receive your 3D drawings (stp step igs iges format) and quote according to your needs such as quantity material surface finish etc.
Before the mold is assembled to the injection molding machine the drawing needs to be programmed so that we can clearly see the process of the material as it enters the mold for further adjustments and modifications.
Rapid prototyping uses SLS or SLA 3D printing technology which can efficiently materialize design concepts very popular in the industry.
After the mold is complete it is assembled into the injection molding machine. During the injection process we check that the machine is functioning properly (or not) make some necessary tool adjustments and generate a new sample.
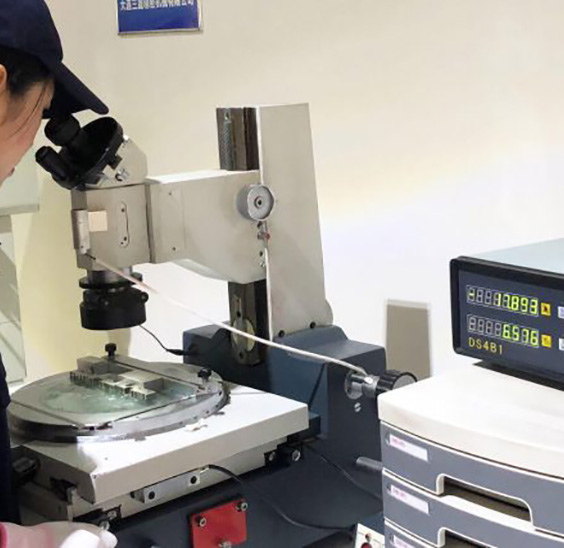
After the samples are surface treated as specified by the customer they will be checked again for dimensions.
According to customer requirements choose the surface treatment method. At the same time quality inspection work is carried out.
The last step is to check whether the mold needs to be adjusted according to the analysis of the sample and whether the test sample meets the previous requirements.
After the samples have been tested to meet the preliminary requirements the samples can be packaged and shipped.
Rapid prototyping is the fast fabrication of a physical part model or assembly using 3D computer aided design (CAD). The creation of the part model or assembly is usually completed using additive manufacturing or more commonly known as 3D printing. Rapid prototyping using selective laser meltingWhere the design closely matches the proposed finished product it is said to be a high fidelity prototype as opposed to a low fidelity prototype where there is a marked difference between the prototype and the final product.
Rapid prototyping (RP) includes a variety of manufacturing technologies although most utilise layered additive manufacturing. However other technologies used for RP include high-speed machining casting moulding and extruding. While additive manufacturing is the most common rapid prototyping process other more conventional processes can also be used to create prototypes.
In this fast-moving modern-day consumer market companies need to develop and introduce new products faster to remain competitive. Since faster product development and technology innovation are key to a company’s success rapid prototyping becomes the most important element of new product development. The following objectives are achieved through rapid prototyping.
The simple answer is “No”. In the modern-day product development process rapid prototyping is commonly used alongside terms like “3D printing” and “additive manufacturing” mainly because 3D printing first came into prominence as a way of making prototypes quickly (Read more on the history of 3D printing). But the 7 types of additive manufacturing technologies have moved along and have made giant strides towards the production of quality parts and might not be the preferred choice for some prototypes due to higher costs.
Reduced design & development time Reduced overall product development cost Elimination or reduction of risk Allows functionality testing Improved and increased user involvement Ability to evaluate human factors and ergonomics
Lack of accuracy Added initial costs Some rapid prototyping processes are still expensive and not economical Material properties like surface finish and strength cannot be matched Requires skilled labour The range of materials that can be used is limited Overlooking some key features because they cannot be prototyped End-user confusion customers mistaking it for the finished project/developer misunderstanding of user objectives
ABS is a low-cost engineering plastic widely used for pre-injection molding prototypes. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: Black neutral matte finish
Consult now
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance engineering plastic with excellent temperature resistance dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 7 days Colors: Natural (off-white)
Consult now
PE is a slippery plastic that is often machined into plugs and seals. It is also an excellent electrical insulator as well as being moisture and chemically-resistant. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: White black
Consult now
In high-stress or high-temperature applications PEEK is a great lightweight plastic substitute for most soft metals. Additionally PEEK is resistant to moisture wear and chemicals. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: Opaque beige Grades: Standard PEEK 30% Glass Filled
Consult now
Acrylic is a scratch-resistant plastic material often used for tanks panels and optical applications. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: Optically clear opaque
Consult now
Delrin or acetal is a low-friction high-stiffness plastic material. With a relatively high toughness and minimal elongation Delrin boasts excellent dimensional accuracy. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: White black brown Grades: 150 AF (13% PTFE Filled) 30% Glass Filled
Consult now
Nylon is a general purpose plastic material that resists both frictional and chemical wear. Two of the most notable use cases for Nylon are in medical devices and electronics insulation notably screws and spacers for panel mounted circuit boards. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days
Consult now
Polypropylene (PP) resists most solvents and chemicals which makes it a wonderful material to manufacture laboratory equipment and containers for a variety of applications. PP also offers good fatigue strength. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Colors: White (semi-clear or opaque)
Consult now
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used metals in the world because of its excellent strength-to-weight ratio low cost and recyclability. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Alloys: 6061-T6 7075-T6 7050 2024 5052 6063 MIC6 Finishing Options: Alodine Anodizing Types II III III + PTFE ENP Media Blasting Nickel Plating Powder Coating Tumble Polishing.
Consult now
JTC offers both alloy and carbon steel options useful for a variety of applications including fixtures mounting plates draft shafts axles torsion bars gears bolts studs shafts and structural applications. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Alloys: 4140 4130 A514 4340 Carbon Steel Types: 1018 Low Carbon 1045 Carbon Zinc-Galvanized Low-Carbon Finishing Options: Black Oxide ENP Electropolishing Media Blasting Nickel Plating Powder Coating Tumble Polishing Zinc Plating
Consult now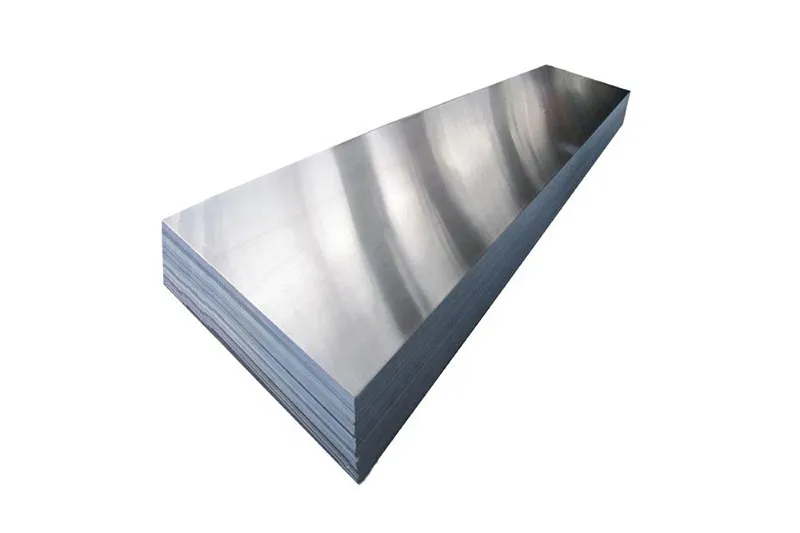
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and rust making it suitable for situations where a part may be exposed to the elements for long period of time. Stainless steel is also fairly malleable and ductile. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 2 days Finishing Options: Black Oxide Electropolishing ENP Media Blasting Nickel Plating Passivation Powder Coating Tumble Polishing Zinc Plating Alloys: 303 304L 316L 410 416 440C 17-4PH Nitronic 60
Consult now
360 Brass also known as free machining brass is commonly used for a variety of parts including gears lock components pipe fittings and ornamental applications. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Finishing Options: Media blasting
Consult now
Cast iron is a dependable wear-resistant material that’s ideal for absorbing vibrations. Great for gears bases pulleys and bushings. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 7 days Finish Options: Media blasting Tumbling
Consult now
101 and 110 copper alloys offer excellent thermal and electrical conductivity which makes them natural choices for bus bars wire connectors and other electrical applications. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Finishing Options: Available as-machined media blasted or hand-polished Alloys: 101 110
Consult now
932 Bearing Bronze is a high strength alloy with good wear and corrosion resistance due to its tin iron and zinc content. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 3 days Finish Options: Available as-machined media blasted or hand-polished
Consult now
Titanium may be selected over other materials such as steel due to its ability to withstand high and subzero temperatures. Common use cases include aerospace fasteners turbine blades engine components sports equipment and marine applications. Mill Lead Time: As fast as 7 days Finishing options: Media Blasting Tumbling Passivation Grade: Titanium Grade 5
Consult now
With excellent wear resistance and toughness it is often used to make fixtures tools tool holders gauges and punches. Factory delivery time: 7 days. Surface treatment: medium spray tumbling black oxide.
Consult now